Overview
The article delves into the concept of agile teams, defining their essence, tracing their evolution, and outlining their guiding principles. It emphasizes their cross-functional nature and adaptability, which are crucial in today's fast-paced environment. By illustrating how agile teams prioritize rapid delivery, embrace change, and foster collaboration, the article underscores the collective impact these elements have on enhancing productivity and responsiveness to client needs. This assertion is supported by various statistics and case studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of agile methodologies.
Introduction
Agile teams have emerged as a transformative force within the landscape of project management, fundamentally reshaping how organizations approach development and delivery. Defined by their cross-functional nature and commitment to adaptability, these teams not only enhance productivity but also foster a culture of collaboration and shared ownership. However, as the demand for agility grows, so too do the challenges associated with implementing effective agile practices.
What are the core principles that underpin these teams? How can they navigate the pitfalls that threaten their success? Exploring the evolution, characteristics, and common obstacles of agile teams reveals a path toward maximizing their potential in an ever-changing environment.
Define Agile Team: Core Concept and Characteristics
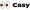
An agile team represents a cross-functional unit typically comprising four to ten members, each equipped with the diverse skills essential for defining, building, testing, and delivering product increments. These agile teams are characterized by self-organization, adaptability, and a strong collaborative spirit. They engage in short cycles known as sprints, which facilitate the continuous delivery of high-quality results. This emphasis on cross-functionality empowers members to take on various roles, fostering a culture of shared responsibility and collective ownership over project outcomes.
Successful agile teams exhibit several key traits:
- They prioritize rapid delivery to customers.
- They sustain high levels of communication.
- They adapt swiftly to changing priorities.
Research indicates that groups that convene frequently for sprints are 24% more responsive and 42% more consistent in the quality of their deliverables. Furthermore, groups focusing on work management reduce the time required by half and experience 75% fewer errors. Organizations that embrace flexible practices report a 47% increase in productivity and a 40% enhancement in project visibility. Notably, 98% of marketers have indicated that their flexible approach has proven successful, underscoring its effectiveness across various sectors.
Case studies underscore the efficiency of agile teams in diverse industries. For instance, the FBI's successful implementation of flexible approaches highlights its capacity for large-scale operations, while the 17th Annual State of Flexible Practices Report reveals that Engineering and Research & Development groups are the fastest-growing adopters of such practices, comprising 48% of practitioners. Additionally, 64% of groups employing iterative methodologies cite enhanced capacity to manage shifting priorities and quicker delivery as primary motivations for their implementation, emphasizing the inherent flexibility of these groups. This trend illustrates the approach's effectiveness in prioritizing delivery and accelerating time to market.
In summary, flexible groups transcend mere practices; they embody a transformative force that reshapes how teams operate, innovate, and deliver value. As Jigar Agrawal aptly noted, "the iterative statistics indicate that it remains the leading methodology, and there are significant improvements in productivity, customer satisfaction, and group empowerment." By cultivating a culture of agility, organizations can profoundly enhance their performance and adaptability in an ever-evolving environment.
Explore the Evolution of Agile Teams: Historical Context
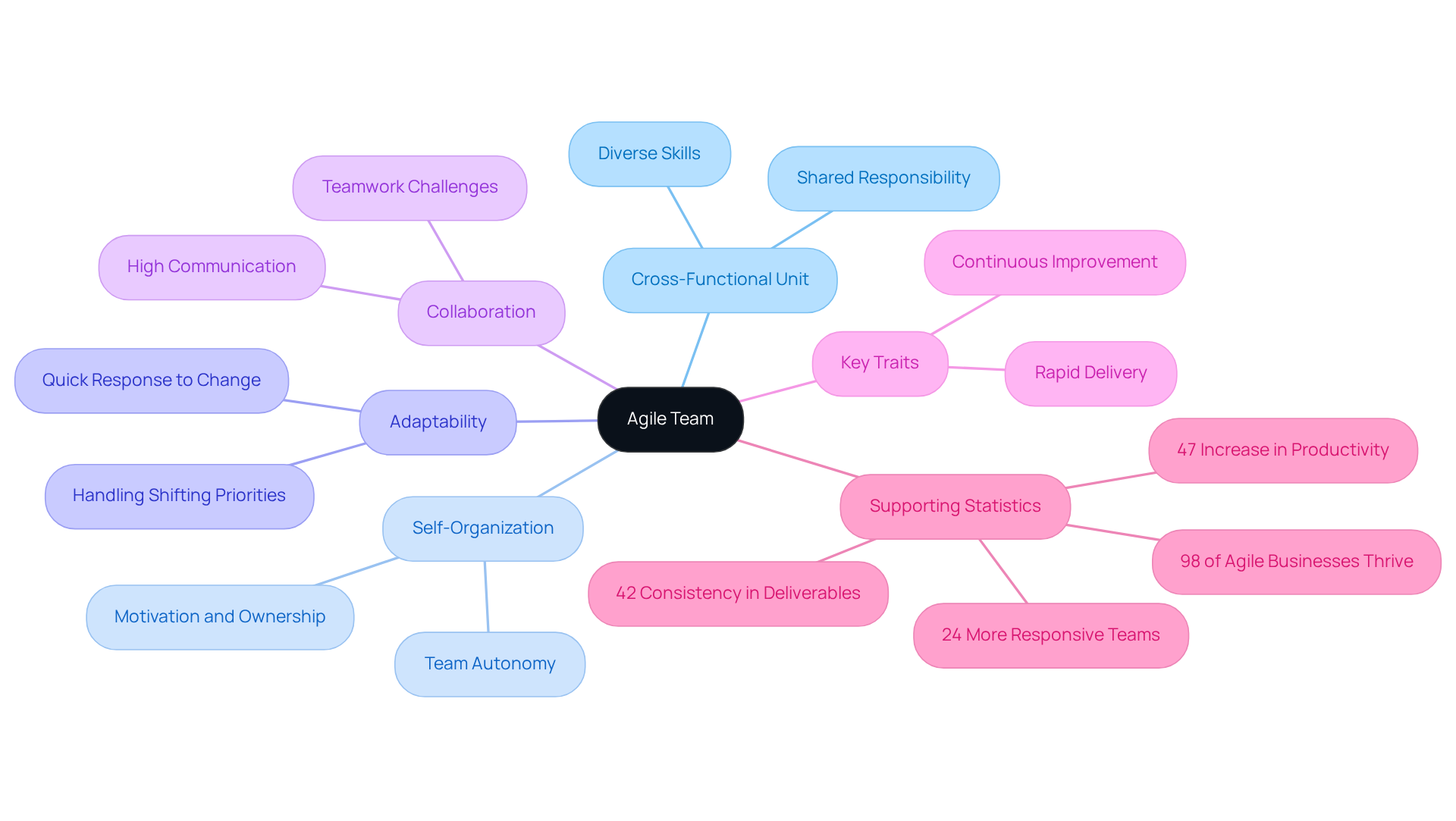
The rise of adaptive teams can be traced back to the late 1990s when software developers sought alternatives to the rigid Waterfall model, often criticized for its inflexibility and inability to respond to changing requirements. This quest for a more adaptable approach culminated in 2001 with the establishment of the Manifesto for Adaptive Software Development by a group of 17 pioneering software creators. This manifesto marked a pivotal moment in the evolution of flexible methodologies, articulating core values such as:
- Prioritizing individuals and interactions over processes and tools
- Emphasizing working software over exhaustive documentation
As flexible methodologies gained traction, teams embraced these principles, leading to the formation of self-managing, cross-disciplinary units capable of swiftly responding to client demands and market shifts. The significance of the Manifesto for Iterative Development in 2025 remains profound, continuing to shape software development practices and influence team structures across various industries. Research shows that organizations employing flexible methodologies report enhanced collaboration and alignment with their objectives, with 93% of these organizations experiencing improved operational performance. Furthermore, the adaptive mindset prioritizes speed, flexibility, and collaboration—qualities essential for navigating today’s fast-paced environment. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of flexible methodologies, compelling teams to adapt rapidly to new challenges. This ongoing evolution underscores the enduring relevance of the Manifesto in fostering a culture of adaptability and continuous improvement within agile teams.
Identify Key Principles of Agile Teams: Values and Practices
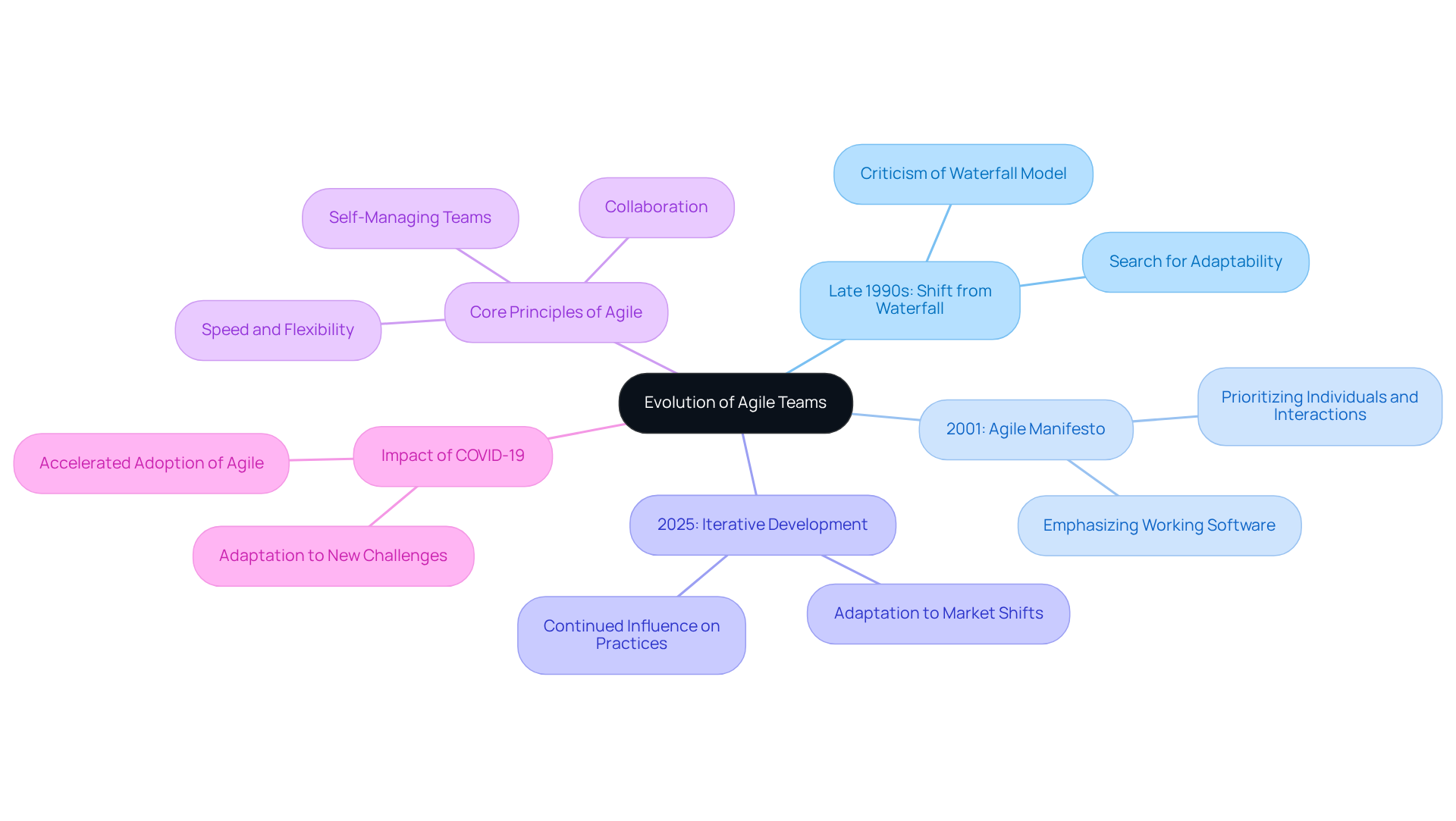
Flexible groups operate under several essential principles that guide their practices, significantly influencing project success and client satisfaction. These principles include:
-
Client Cooperation: An agile team prioritizes client feedback and collaboration throughout the development process, ensuring that the final product meets user needs. This focus on customer-centricity is crucial; studies show that 93% of flexible organizations report increased customer satisfaction.
-
Embracing Change: Flexibility is a cornerstone for an agile team and Agile methodologies. An agile team remains receptive to changing requirements, even late in the development cycle, enabling them to adapt to new information and market dynamics. This adaptability is vital in today’s rapidly evolving landscape, where 33% of groups identify frequent strategy changes as a significant challenge.
-
Iterative Development: Work progresses in short cycles, or sprints, allowing teams to deliver functional increments of the product regularly and gather feedback. This iterative approach enhances the responsiveness of the agile team and facilitates mid-course adjustments based on real-time insights, which is essential for aligning with customer expectations. Pioneer Jim Highsmith emphasizes that successful integration hinges on value delivery rather than strict adherence to methodology.
-
Self-Organization: An agile team consists of flexible groups empowered to make decisions and manage their tasks autonomously, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. This autonomy promotes innovation and boosts team morale, leading to improved project outcomes.
-
Continuous Improvement: Regular reflection on processes and outcomes is fundamental to flexible methodologies. Teams participate in retrospectives and feedback loops to pinpoint areas for enhancement, driving efficiency and effectiveness. This commitment to ongoing improvement is supported by the fact that 76% of agile teams report increased employee engagement, which is critical for sustaining high performance.
By adhering to these principles, flexible groups not only enhance their operational efficiency but also ensure they remain aligned with customer needs, ultimately driving project success.
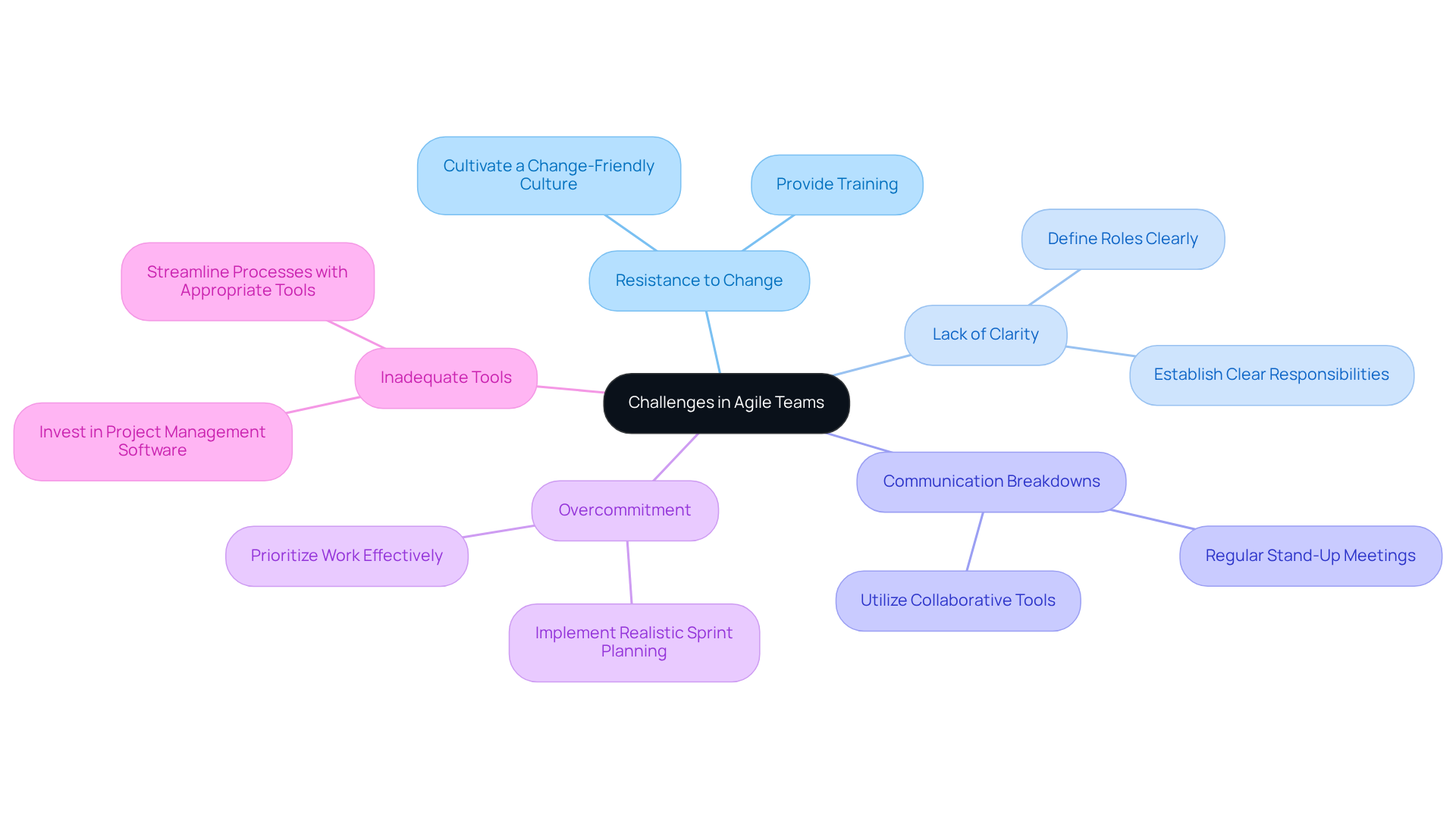
Examine Challenges in Agile Teams: Common Pitfalls and Solutions
Despite their advantages, agile teams often face several challenges that can hinder their effectiveness.
-
Resistance to Change: Team members accustomed to conventional project management may resist adopting new methodologies. Organizations must provide training and cultivate a culture that embraces change to overcome this hurdle.
-
Lack of Clarity: Agile teams may grapple with ambiguous roles and responsibilities, resulting in confusion and inefficiency. Clearly defining roles, such as Product Owner and Scrum Master, within the agile team is essential to mitigate this issue.
-
Communication breakdowns can happen, but effective communication is crucial for agile teams. Regular stand-up meetings and collaborative tools can enhance communication and ensure alignment among the agile team members.
-
Overcommitment: Teams may take on excessive work during sprints, leading to burnout and a decline in quality. For an agile team, implementing realistic sprint planning and prioritization techniques is vital for managing workload effectively.
-
Inadequate Tools: Without the right tools to support Agile practices, teams may struggle to maintain efficiency. Investing in appropriate project management software can streamline processes and enhance collaboration, ultimately driving success.
Conclusion
Agile teams embody a transformative approach to project management, defined by their cross-functional nature, self-organization, and adaptability. By prioritizing collaboration and rapid delivery, these teams cultivate a culture of shared responsibility, enabling effective responses to changing requirements and customer needs. This flexibility transcends mere methodology; it signifies a fundamental shift in how teams operate, innovate, and deliver value in today's fast-paced environment.
Key insights from this discussion highlight the evolution of agile teams, tracing their origins back to the late 1990s and the groundbreaking principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto. The focus on client cooperation, iterative development, and continuous improvement has demonstrably enhanced project success and customer satisfaction. Furthermore, challenges such as resistance to change and communication breakdowns can be effectively mitigated through targeted training, clear role definitions, and appropriate tools, ensuring agile teams can flourish.
Ultimately, adopting agile methodologies is vital for organizations aiming to boost their performance and adaptability. The continuous evolution of agile practices emphasizes the necessity of fostering a culture of agility, which not only propels productivity but also empowers teams to navigate the complexities of modern project management. By prioritizing agility, organizations position themselves for sustained success and innovation in an ever-evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an agile team?
An agile team is a cross-functional unit that typically consists of four to ten members, each possessing diverse skills necessary for defining, building, testing, and delivering product increments.
What are the key characteristics of agile teams?
Agile teams are characterized by self-organization, adaptability, strong collaboration, and a culture of shared responsibility and collective ownership over project outcomes.
How do agile teams work?
Agile teams engage in short cycles known as sprints, which enable the continuous delivery of high-quality results.
What traits do successful agile teams exhibit?
Successful agile teams prioritize rapid delivery to customers, maintain high levels of communication, and adapt swiftly to changing priorities.
What are the benefits of frequent sprint meetings for agile teams?
Research shows that groups that meet frequently for sprints are 24% more responsive and 42% more consistent in the quality of their deliverables.
How does focusing on work management impact agile teams?
Focusing on work management can reduce the time required for tasks by half and lead to 75% fewer errors.
What improvements do organizations experience by adopting flexible practices?
Organizations that embrace flexible practices report a 47% increase in productivity and a 40% enhancement in project visibility.
Are there specific industries that benefit more from agile practices?
Yes, case studies show that industries such as Engineering and Research & Development are the fastest-growing adopters of agile practices, comprising 48% of practitioners.
What motivations do groups have for employing iterative methodologies?
64% of groups using iterative methodologies cite enhanced capacity to manage shifting priorities and quicker delivery as primary motivations for their implementation.
What overall impact do flexible agile teams have on organizations?
Flexible agile teams act as a transformative force that reshapes how teams operate, innovate, and deliver value, leading to significant improvements in productivity, customer satisfaction, and group empowerment.