Overview
This article delves into the effective prioritization of tasks through the Eisenhower Matrix, a strategic tool that categorizes tasks into four distinct quadrants based on urgency and importance. By employing this method, individuals and teams can significantly enhance productivity while simultaneously reducing stress levels. It facilitates the identification and concentration on high-impact activities, ensuring that efforts are directed where they matter most. Moreover, it is essential to regularly reassess priorities, adapting to the ever-changing circumstances that arise in both personal and professional environments.
Introduction
Understanding how to prioritize tasks is essential for unlocking greater productivity and alleviating workplace stress. The Eisenhower Matrix serves as a powerful framework for task management, enabling individuals and teams to differentiate between what is urgent and what is important. This distinction ultimately guides them to concentrate on high-impact activities.
Yet, with a multitude of responsibilities vying for attention, how can one effectively integrate this matrix into their daily workflow without succumbing to overwhelm? It's a challenge that many face, but with the right strategies, it can be overcome.
Understand Task Prioritization
It is crucial to understand how to prioritize tasks for evaluating the importance of different assignments. It helps individuals and groups understand how to prioritize tasks by determining which require urgent focus and which can be scheduled for later. This practice is essential for learning how to prioritize tasks, boosting productivity and ensuring that significant activities are completed promptly. Understanding how to prioritize tasks by recognizing the distinction between urgent and important tasks enables groups to make informed decisions about where to concentrate their efforts.
For instance, learning how to prioritize tasks based on their urgency and significance can lead to enhanced group performance. This approach provides guidance on how to prioritize tasks efficiently while reducing stress levels. Productivity specialists emphasize how to prioritize tasks, stating that effective prioritization clarifies roles and responsibilities, fostering a supportive group atmosphere that enhances collaboration.
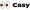
Real-world examples, such as the application of the Eisenhower Matrix, illustrate how groups can categorize activities into four quadrants:
- Urgent and Important
- Important but Not Urgent
- Urgent but Not Important
- Neither Urgent Nor Important
This method not only helps in identifying genuine urgencies but also supports groups in avoiding the pitfalls of constant fire-fighting and excessive workloads.
By regularly evaluating the importance of activities and understanding how to prioritize tasks, teams can maintain focus on what truly matters. This ultimately leads to a more organized and less stressful work environment. Significantly, nearly 47 percent of employees report feeling overburdened or anxious at work, underscoring the importance of efficient prioritization in alleviating stress.
Moreover, it is vital to consistently re-evaluate priorities to adapt to changing circumstances and avoid the sunk cost fallacy, which can impede productivity. As productivity specialist Tim Cook states, 'Getting up early might be intimidating for many, but studies indicate that leaders awaken early to prioritize their responsibilities efficiently.
Utilize the Eisenhower Matrix
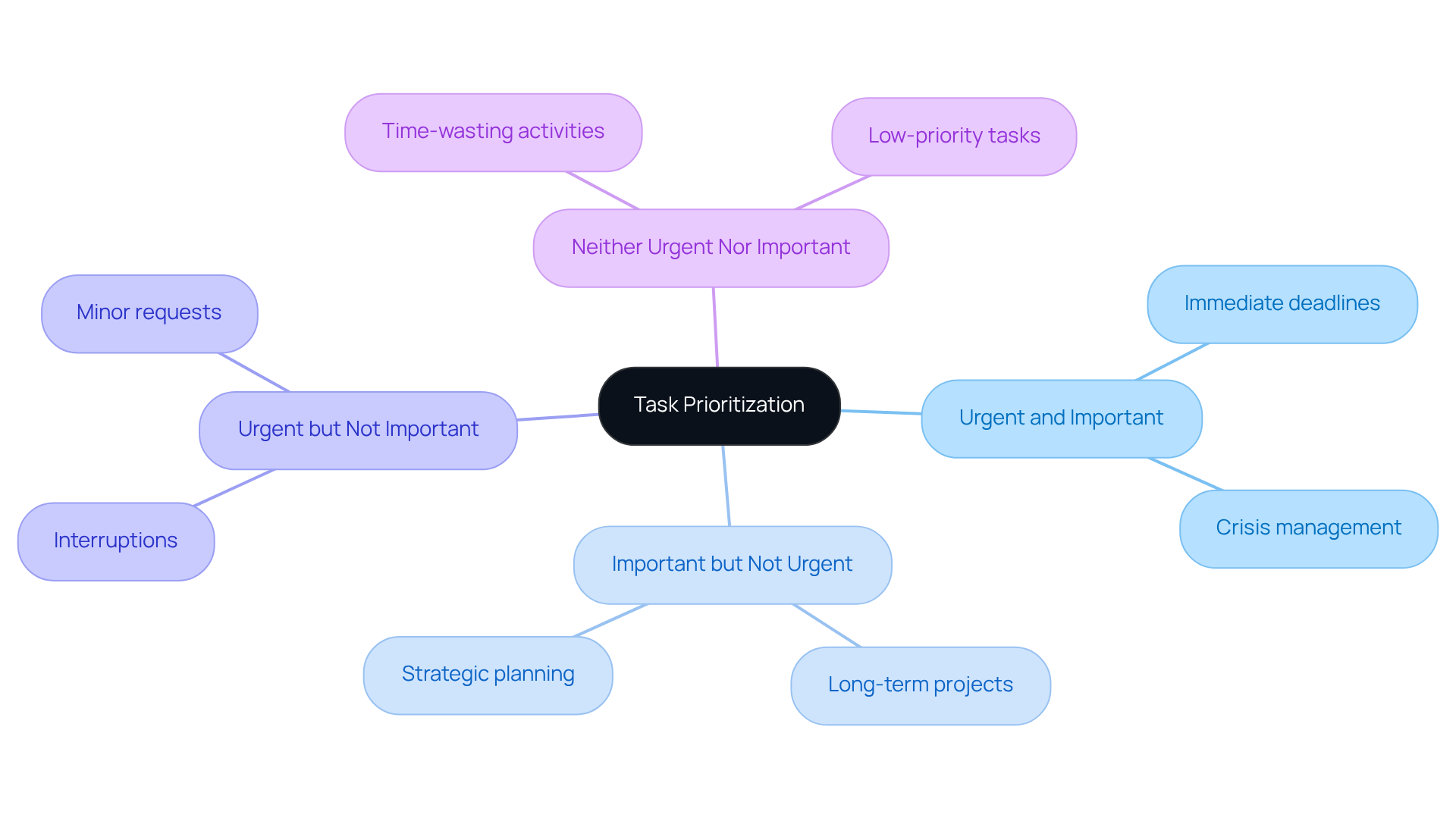
The Eisenhower Matrix serves as a robust tool for prioritizing tasks by categorizing them into four distinct quadrants based on urgency and importance:
- Critical and Significant (Address First): Activities in this quadrant demand immediate attention and have significant repercussions if not executed promptly. For instance, an approaching project deadline necessitates swift action to avoid penalties.
- Essential yet Not Immediate (Schedule): This category encompasses tasks vital for long-term success that do not require immediate action. Scheduling time for strategic planning or professional development can foster substantial growth over time. As Cassidy Horton aptly states, "Remember, the key to truly satisfying success lies in not only managing the urgent, but also investing time and energy in what truly matters in the long run."
- Urgent but Not Important (Delegate): These activities may require prompt attention but are not essential to your primary objectives. Delegating responsibilities, such as routine administrative tasks, allows you to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Not Urgent and Not Important (Delete): Tasks that do not contribute to your objectives should be eliminated. This may include excessive social media browsing or attending meetings that lack clear agendas.
By effectively organizing activities using the Eisenhower Matrix, professionals can learn how to prioritize tasks, significantly enhancing their productivity and ensuring they concentrate on what truly matters. Teams that have embraced this framework report improved focus and reduced stress, as they can prioritize their efforts on high-impact activities. Current usage rates indicate that numerous professionals are leveraging the Eisenhower Matrix to optimize their workflows, recognizing its importance in managing both urgent and significant tasks. Expert insights underscore that mastering this matrix not only aids in immediate project management but also fosters long-term strategic thinking, ultimately yielding greater success. Furthermore, utilizing Casy can enhance the implementation of the Eisenhower Matrix by automating project management, enabling teams to focus on development and innovation rather than becoming overwhelmed by project management complexities.
Implement the Eisenhower Matrix in Your Workflow
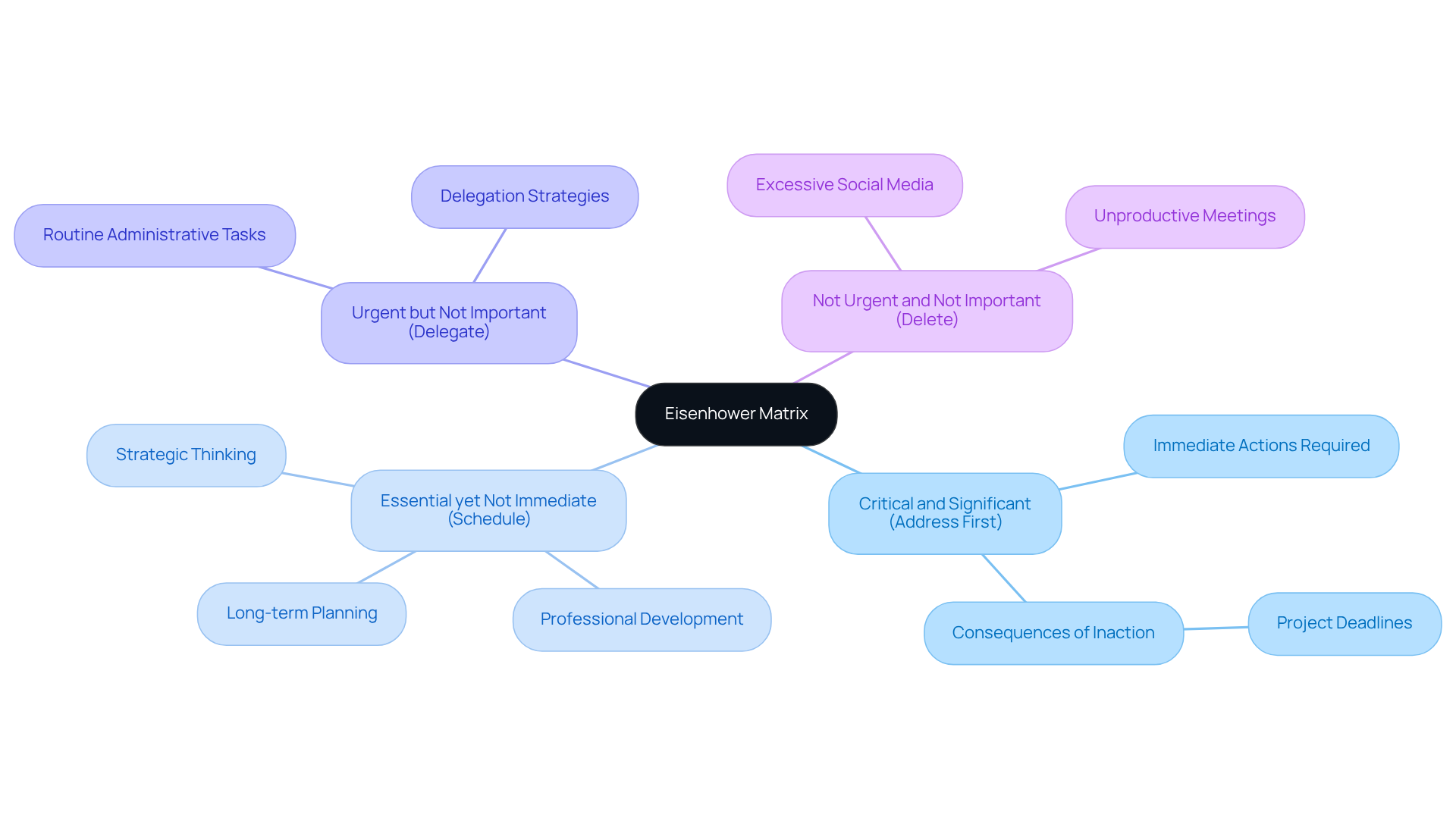
To effectively implement the Eisenhower Matrix in your workflow, follow these steps:
- Create a To-Do List: Begin by compiling a comprehensive list of all activities you need to complete. Utilize a digital tool like Casy or a simple notepad to capture everything.
- Categorize Tasks: Review your list and assign each task to one of the four quadrants of the Eisenhower Matrix:
- Urgent and Important (Do First): These tasks require immediate attention and have significant consequences if not completed. For instance, finalizing a blog post due today.
- Not Urgent but Important (Schedule): These tasks contribute to long-term goals and should be planned for later. Consider creating an editorial calendar for the next quarter.
- Urgent but Not Important (Delegate): Tasks that need to be done soon but can be assigned to someone else. An example is responding to non-urgent media inquiries.
- Neither Urgent nor Important (Delete): Tasks that do not add value and should be eliminated to maintain focus. For example, scrolling through social media feeds aimlessly.
- To understand how to prioritize tasks, focus on activities in the 'Do First' quadrant and assign specific time slots in your schedule for 'Schedule' activities. Identify team members who can take on 'Delegate' activities, and simply remove 'Delete' items from your list.
- Review Regularly: At the end of each day or week, revisit your matrix to reassess and adjust priorities based on new responsibilities or changes in urgency and importance.
As Ng emphasizes, being methodical about activity selection is crucial for effective time management. By consistently employing this organized method, you can significantly enhance your focus and productivity, while also learning how to prioritize tasks to ensure that you remain engaged with the most important activities. This approach not only aids in managing daily responsibilities but also aligns with long-term objectives, fostering a more organized and efficient workflow.
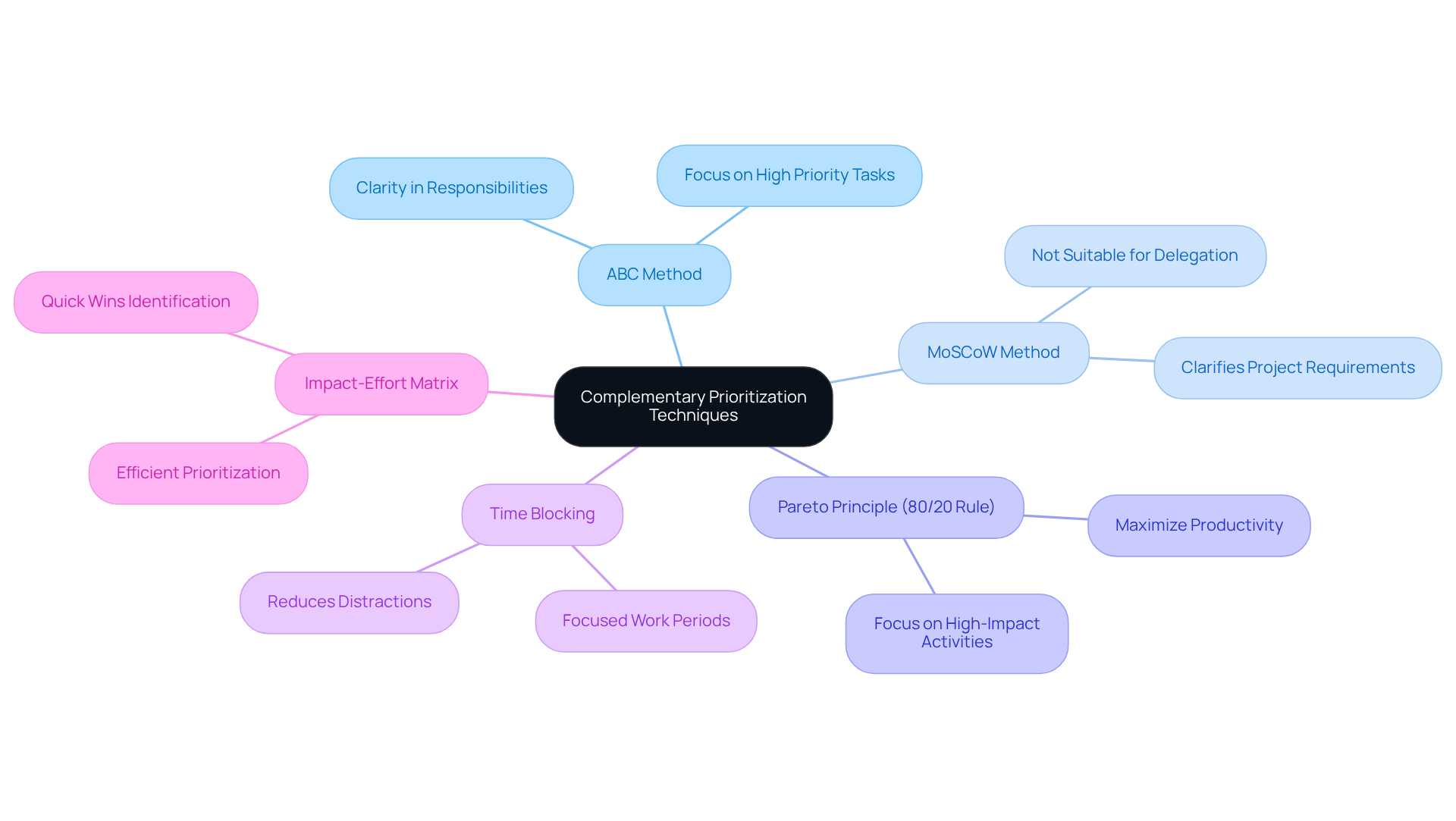
Explore Complementary Prioritization Techniques
In addition to the Eisenhower Matrix, consider these complementary prioritization techniques that can significantly enhance your productivity:
-
ABC Method: This technique involves assigning an 'A', 'B', or 'C' to each activity based on its importance, with 'A' representing the highest priority. Productivity specialists emphasize that the ABC method promotes clarity in managing responsibilities, demonstrating how to prioritize tasks and enabling teams to focus on what genuinely counts. As noted by a productivity expert, "Effective prioritization relies on clarity, collaboration, and regular adjustments."
-
MoSCoW Method: This approach classifies activities into Must have, Should have, Could have, and Won't have. While it assists in clarifying priorities according to project requirements, it's crucial to note that the MoSCoW method may not be suitable for activities that necessitate delegation. In such cases, the ABCDE method serves as a more refined alternative. By clarifying how to prioritize tasks, groups can effectively allocate resources and time to the most significant activities, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes.
-
Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule): This principle suggests concentrating on the 20% of activities that will produce 80% of the outcomes. By understanding how to prioritize tasks and recognizing high-impact activities, groups can maximize productivity and ensure that their efforts are directed towards achieving significant results.
-
Time Blocking: This method entails designating specific time segments for various activities or categories of activities. By scheduling focused periods for work, individuals can maintain concentration and reduce distractions, leading to improved efficiency.
-
Impact-Effort Matrix: This matrix evaluates activities based on the effort required and the potential impact of completion, assisting groups in prioritizing work efficiently. Tasks that demand low effort but yield high impact should be prioritized for quick wins.
By combining these techniques with the Eisenhower Matrix, you can learn how to prioritize tasks and develop a robust strategy that enhances your productivity and effectiveness. Additionally, identifying your most productive times of day for completing activities can further refine your approach. Real-world examples illustrate the ABC method's effectiveness in task prioritization; groups that apply it often report clearer focus and enhanced task completion rates. This organized method not only aids in managing workloads but also fosters a culture of responsibility and transparency among teams. Continuous prioritization and regular adjustments are essential to adapt to changing circumstances and maintain alignment with team goals.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of task prioritization is essential for enhancing productivity and achieving long-term goals. The Eisenhower Matrix serves as an invaluable tool, enabling individuals and teams to distinguish between urgent and important tasks. By effectively categorizing activities, one can focus on what truly matters, thus fostering a structured and less stressful work environment.
Key insights from this guide highlight the importance of:
- Regularly assessing tasks
- Utilizing the four quadrants of the Eisenhower Matrix
- Implementing complementary prioritization techniques like the ABC method and the Pareto Principle
These strategies not only streamline workflows but also promote a culture of collaboration and accountability within teams.
Ultimately, the significance of efficient task prioritization cannot be overstated. Embracing these methods empowers individuals to make informed decisions, reduce overwhelm, and align daily activities with overarching objectives. By committing to a systematic approach to prioritization, professionals can enhance their effectiveness and drive meaningful progress in both personal and professional realms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is task prioritization important?
Task prioritization is important because it helps individuals and groups evaluate the importance of different assignments, determine which tasks require urgent focus, and boost productivity by ensuring significant activities are completed promptly.
How can understanding task prioritization improve group performance?
Understanding task prioritization can enhance group performance by providing guidance on efficiently focusing efforts, reducing stress levels, clarifying roles and responsibilities, and fostering a supportive atmosphere that enhances collaboration.
What is the Eisenhower Matrix, and how does it help with task prioritization?
The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool that categorizes activities into four quadrants: Urgent and Important, Important but Not Urgent, Urgent but Not Important, and Neither Urgent Nor Important. It helps identify genuine urgencies and supports groups in avoiding constant fire-fighting and excessive workloads.
What are the benefits of regularly evaluating task priorities?
Regularly evaluating task priorities helps teams maintain focus on what truly matters, leading to a more organized and less stressful work environment. It also allows for adaptation to changing circumstances and helps avoid the sunk cost fallacy, which can impede productivity.
How prevalent is the issue of feeling overburdened or anxious at work?
Nearly 47 percent of employees report feeling overburdened or anxious at work, highlighting the importance of efficient prioritization in alleviating stress.
What does Tim Cook suggest about early rising and task prioritization?
Tim Cook suggests that getting up early might be intimidating, but studies indicate that leaders who wake up early can prioritize their responsibilities efficiently.